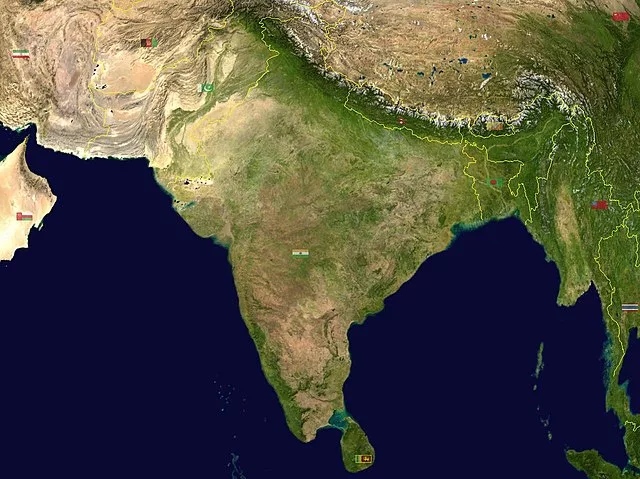
India, a nation located in South Asia, is often referred to as a subcontinent due to its remarkable geographical features, historical significance, and cultural diversity. Let’s explore the factors that justify this unique distinction.
Table of Contents
Geographical Features of India
India’s geography is vast and diverse, encompassing various landforms and natural features. The country stretches from the Himalayan mountain range in the north to the Indian Ocean in the south. Some of the prominent geographical aspects that make India a subcontinent are:
Vast Size and Diverse Landforms:
India is the seventh-largest country in the world, covering a substantial area of the Asian continent. It boasts diverse landforms, including mountains, plateaus, plains, and coastal regions, each contributing to its distinct identity.
Similar read: Who Owns Instagram?
Himalayan Barrier:
The mighty Himalayas, known as the “Roof of the World,” act as a natural barrier to the north of India. These towering mountains not only provide a breathtaking landscape but also play a significant role in shaping India’s climate, culture, and historical interactions.
Peninsular Plateau:
South of the Himalayas lies the peninsular plateau, comprising rocky terrain and fertile river valleys. This vast plateau covers a considerable portion of India and adds to the subcontinent’s geographic uniqueness.
Coastal Plains and Islands:
India is blessed with extensive coastal plains along the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. These plains are dotted with bustling cities, picturesque beaches, and tropical islands such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, further enhancing India’s subcontinental character.
Historical Significance
India’s history spans several millennia and encompasses ancient civilizations, powerful empires, and cultural exchanges. The historical significance of India supports its identification as a subcontinent. Key historical factors include:
Ancient Civilizations and Empires:
India is the birthplace of one of the world’s oldest civilizations. The Indus Valley Civilization, dating back to the Bronze Age, thrived in the Indus River basin. Subsequently, various empires, such as the Maurya, Gupta, and Vijayanagara, left an indelible mark on Indian history.
Similar read: Why Earth Is Called The Blue Planet?
Influence of Buddhism and Hinduism:
India is the birthplace of major religions like Buddhism and Hinduism. The teachings of Buddha and the development of Hindu philosophy have had a profound impact on the world, making India an important spiritual and philosophical hub.
Mughal Empire:
The Mughal Empire, which spanned from the 16th to the 19th century, played a crucial role in shaping India’s history and cultural heritage. The Mughals left behind magnificent architectural wonders like the Taj Mahal, showcasing their architectural prowess.
Cultural Diversity
India is renowned for its cultural diversity, with numerous languages, religions, traditions, and artistic expressions coexisting harmoniously. This vibrant cultural tapestry reinforces its subcontinental identity. Key aspects of India’s cultural diversity include:
Linguistic Diversity:
India is a linguistic paradise, with more than 1,600 languages spoken across its length and breadth. This linguistic diversity is a testament to the country’s multicultural fabric.
Religious Plurality:
India is home to several major religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism, among others. This religious plurality fosters a spirit of tolerance, coexistence, and mutual respect.
Festivals and Traditions:
India celebrates a plethora of colorful festivals throughout the year, showcasing the unity and diversity of its people. Festivals like Diwali, Holi, Eid, Christmas, and Pongal bring communities together and highlight India’s cultural richness.
Art and Architecture:
India’s art and architecture are renowned worldwide. From ancient cave paintings to magnificent temples, palaces, and forts, the country’s architectural marvels are a testament to the creativity and craftsmanship of its people.
Unity in Diversity
India’s subcontinental character is further reinforced by the unity that exists amidst its incredible diversity. Despite the variations in language, religion, and cultural practices, India has managed to forge a strong national identity. Factors that contribute to this unity include:
Indian National Identity:
Indians share a sense of pride and belongingness toward their country. The concept of “unity in diversity” forms the cornerstone of the Indian national identity, promoting inclusivity and social cohesion.
Political Integration:
India’s political history involves the unification of several princely states and territories to form a unified nation. This process of political integration exemplifies India’s ability to overcome regional differences and forge a united nation.
Similar read: What Is A Thesis
Shared History and Values:
India’s people share a rich history and common values, including principles of non-violence, respect for elders, and hospitality. These shared values form the bedrock of Indian society and contribute to its subcontinental character.
Conclusion
India is rightfully called a subcontinent due to its unique blend of geography, history, and culture. Its vast size, diverse landforms, ancient civilizations, religious plurality, and shared national identity are all factors that contribute to this distinction. India’s subcontinental status is a testament to its rich heritage and the remarkable tapestry of its people.
FAQ:
What does the term "subcontinent" mean?
The term "subcontinent" refers to a large, distinct landmass that is part of a larger continent but has its unique geographical, historical, and cultural characteristics.
What are some famous cultural festivals in India?
Some famous cultural festivals in India include Diwali, Holi, Eid, Christmas, Navratri, Durga Puja, and Ganesh Chaturthi.
How many languages are spoken in India?
India is home to more than 1,600 languages, including major languages like Hindi, Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, and Gujarati.
What is the significance of the Himalayas in India?
The Himalayas act as a natural barrier, shaping India's climate, protecting it from cold winds, and influencing the country's cultural and historical interactions.
What are some famous historical landmarks in India?
Famous historical landmarks in India include the Taj Mahal, Red Fort, Qutub Minar, Jaipur's City Palace, and Khajuraho Temples.
- What is Epic Games Launcher and How to Install It? - July 15, 2024
- What Is Audius Music Streaming App and How Does it Work? - July 13, 2024
- The 10 Best Astronomy Apps for Stargazing - July 12, 2024