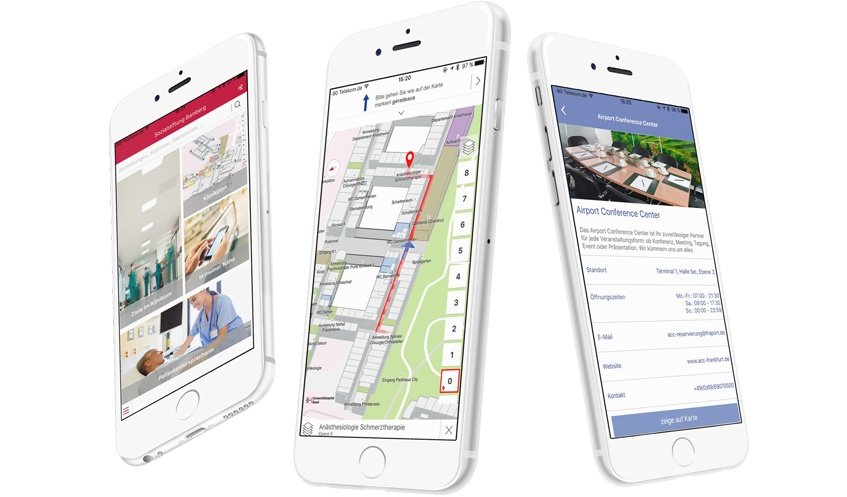
Have you ever thought of reaching a new place without seeking help from GPS? Probably not! Do you think GPS systems are for outdoors or do they provide any assistance in those large building like airports, malls, or conference centers? To prevent yourself from getting hopelessly lost, you need to consider some of the Best Indoor Navigation Apps for Android.
Table of Contents
What are Indoor Navigation Apps?
As the name implies, these apps create interactive maps and navigation tools that can be used by others on their smartphones. Being no longer a luxury, smartphones today features a variety of sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes, electronic compasses, barometers, etc.
So what do these apps do they simply access those sensors and the environment around you? A map is being created that can help you to move your desired location within the building quickly and easily. No matter how confusing the road or building is, you will find your way!
Best Indoor Navigation Apps Android
Further below I would like you to get acquainted with certain apps that enhance the use of indoor navigation technology across the globe.
1. Path Guide
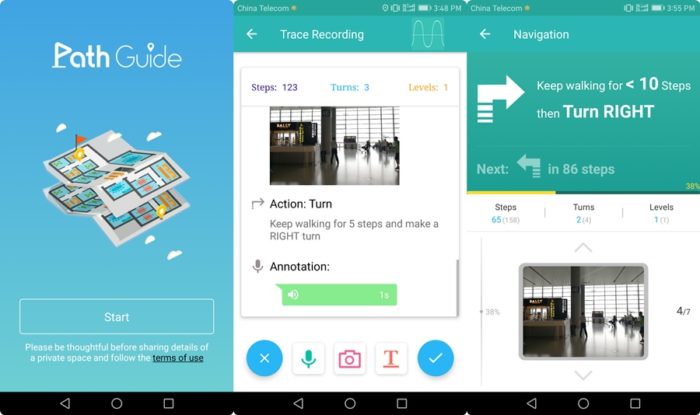
Have you ever played “Follow the Leader”? Path guide is quite similar plug-and-play indoor navigation app where one person creates a map of building and uploads to the cloud so that others can easily download it. After compiling data from a wide array of users, the Android app can amplify the benefits of every single path collected.
Without using GPS signals, the mapping is done by your motion within a building in particular. Technically speaking, it uses your phone’s barometer and magnetometer to calculate distances and create maps of the location you are mapping.
2. Google Indoor Maps
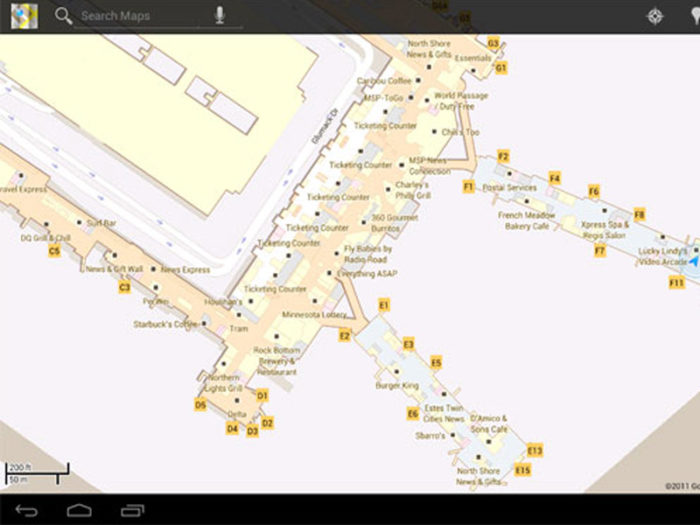
Featuring some indoor maps in its regular apps, Google indoor maps allow you to see the locations of various things located in a building (only the ones which have indoor maps in the Google Maps directory).
Google indoor maps is beneficial for certain buildings such as airports, bus bays, shopping malls, stadiums and so more. It may quite interest you to know that you don’t need any special app to use it as all the buildings are shown on Google maps.
However, it does not navigate like its road app does, but it does give you a way to find your destination.
3. IndoorAtlas MapCreator 2
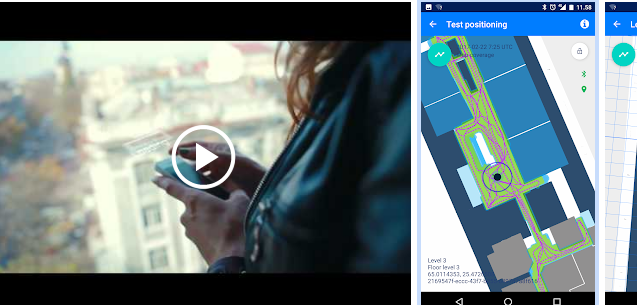
In this Indoor Navigation app, most of your work will be done on your PC. With the help of gyroscope on your phone, all the pathways are recorded. All you have to do is add buildings and create maps from the IndoorAtlas website. Steps are pretty much easier in comparison to other apps, but you need to do it on your PC.
4. Anyplace Indoor Service
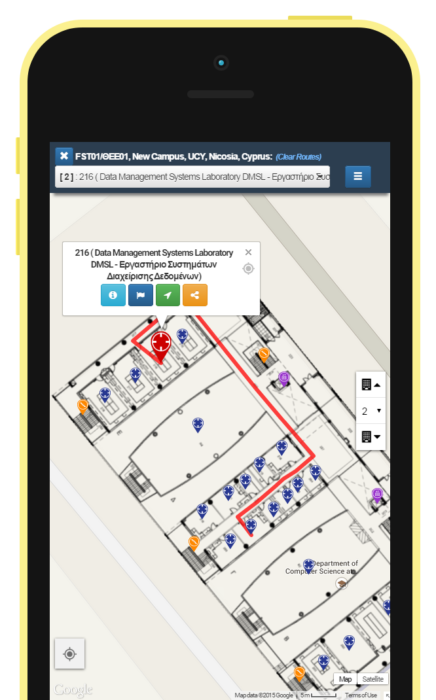
Available on GitHub, the app is a free and open source project which is known to make adding a new building in as little as 1 second. Staring from adding floor plans to images, POIs (points of interests), and use the campus mode to signify whether the building is part of a group.
Hence, navigating within the building becomes easy. In fact, Anyplace Indoor Service claims that their API and tech is accurate to 1.96 meters which is really impressive and should be more than enough to help you reach where you want.
Also, the mobile app seems to have won a number of international awards for its design and implementation. Apart from Android, it is also available on Windows.
5. Situm Mapping Tool
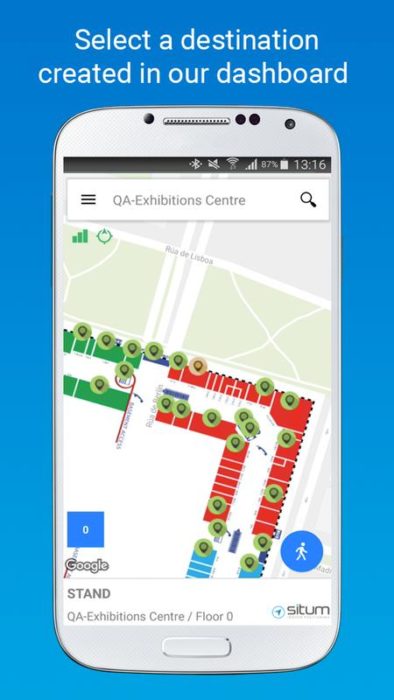
It is an enterprise level software tool that is mainly used for corporate indoor navigation, mapping, and sharing. The indoor navigation app successfully stores and shares the indoor map of your building with its end users.
To get started with the app, all you have to do is go to the Situm Dashboard webpage and create an account firstly. Then you can choose any location from the map and start adding buildings.
As soon as you do this, you will start using the app you will see created locations or buildings. However, you need to upload the floor map manually. It will be attached to your building on the entire map, and there you will be able to set the navigation.
All you have to do is choose a spot and record the pathways between locations. Situm Mapping Tool itself calculates the distance by movements and turnings.
With the combined mean of the gyroscope, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, the app will accurately create indoor maps for you. The app has a tutorial section within, which could lead you through the mapping procedures.
6. Indoorway

Another enterprise level software suitable for those who wish to create an accurate map for the public. So far there is no stand-alone application when you wish to record and save maps on your phone.
With the help of a web dashboard, one can manage and share the maps and navigations. It becomes easy to create your maps as Indoorway uses Google business listing data to find your business.
Also, it uses Bluetooth as its mapping system so make sure you have at least 28-30 Bluetooth beacons to create maps with accurate height and area information.
Best Indoor Navigation Apps : Conclusion
So that’s all for now! These are some of the most interesting indoor navigation apps to take into account. Whether you are an owner or end user, these apps can create maps, POIs, add images and of course, find your way around to make things way easier for you like never before. Either way, these best free navigation apps are super helpful and quickly changing the way we go about doing our business when moving inside buildings.
- Top 6 Best Indoor Navigation Apps for Android - April 3, 2019